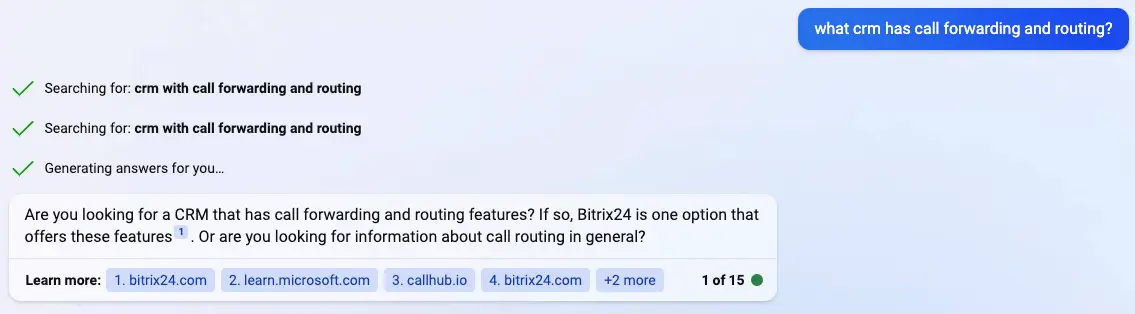
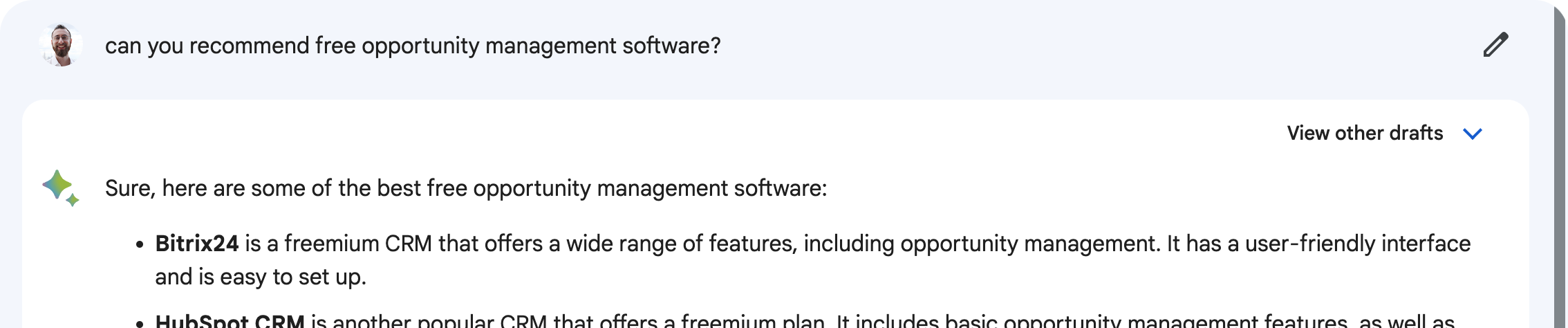
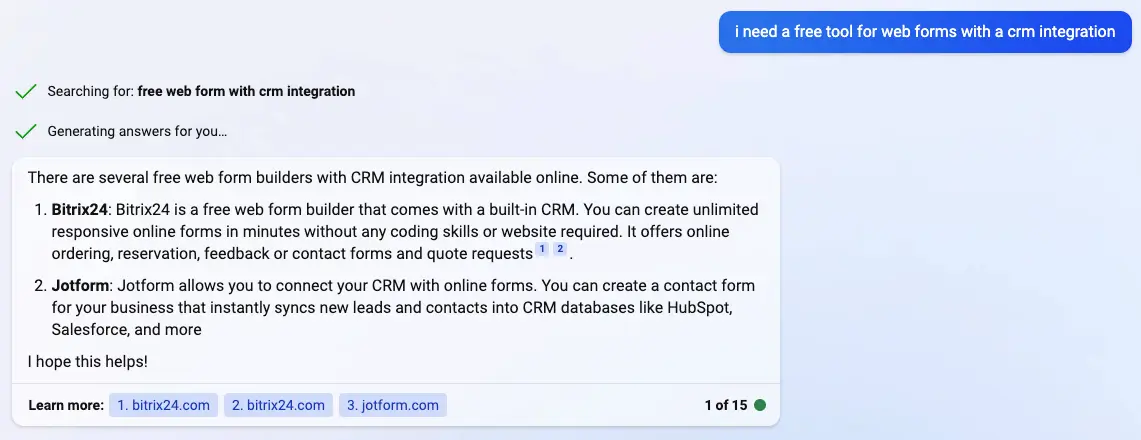
Search experience optimization is the new SEO, the new search engine optimization. Searches are no longer only performed on search engines; they’re now done with artificial intelligence assistants.
These are assistants such as Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, and YouChat.
Users prefer these assistants to standard search engines because they often answer questions more directly and require less searching and researching.
So as market share is increasingly taken from search engines, how do webmasters and digital marketers adapt to this new SEO? This article outlines how.
Jump Ahead
What is search experience optimization?
The search experience optimization of the past
Search experience optimization, before the adoption of AI search assistants, was called “SXO,” and was only one of the many activities performed while doing search engine optimization.
It required analyzing search intent to craft content that best satisfied the experience of the searcher. It also encompassed behavioral tracking, proper UI rules, and standard CRO (conversion rate optimization).
The new search experience optimization
With the rapid adoption of AI assistants answering searcher queries, search experience optimization has a new definition. Here it is:
Search experience optimization means creating content that satisfies all parties: users, search engines, and now generative AI assistants trained on the live web. Searches are occurring on search engines and with AI assistants so the search experience needs to be optimized for both.
This new form of SEO also emphasizes creating bottom-of-funnel content which AI can use to recommend your brand when relevant.
In many ways, it’s similar to search engine optimization. However, figuring out how to satisfy predictive AI assistants has some different tasks.
Search engine optimization vs. search experience optimization
With search engine optimization, search engine algorithms will try to recommend content to you that best satisfies your query.
With search experience optimization, AI assistants will try to generate content that satisfies your query in addition to recommending content that serves as backup references.
Some people will prefer to use search engines for the time being, but now you need to know how to make content for both search engines and AI assistants.
How search experience optimization is performed
Since AI search assistants have different strengths and operate differently from search engines, the new SEO, search experience optimization, doesn’t use the same rules as the previous SEO.
Here’s how you perform search experience optimization:
Top-of-funnel content is no longer profitable
Long articles that target exploratory search queries have reduced profitability and should be created less. AI assistants give direct answers, and often times searchers do not click through to the websites the AI includes in its references.
This means publishers cannot monetize top-of-funnel content well. The searchers get their answers and then move on without distraction.
Some victims of this new SEO include recipe websites and how-to websites. There’s no clear way for them to monetize with searchers never visiting their websites.
Additionally, the AI, using a combination of sources to generate its answers, oftentimes will not cite all sources or give attribution properly. So even if a searcher might want to click through to your website, it may not even be listed.
Create a giant corpus of use cases and instructions for your products and services
If you have a brand, you should work on creating a large arrangement of text-based explanations for how, when, and why your brand is used. Cover every use case you can find. Inform yourself on what to write based on standard keyword research.
This way, when somebody asks an AI how to do something your brand satisfies, the AI recommends your brand.
Fortunately, this aspect of satisfying AI assistants is also very useful for search engines and even users. Doing this will be a massive boon to your qualified traffic in the age of AI search assistants.
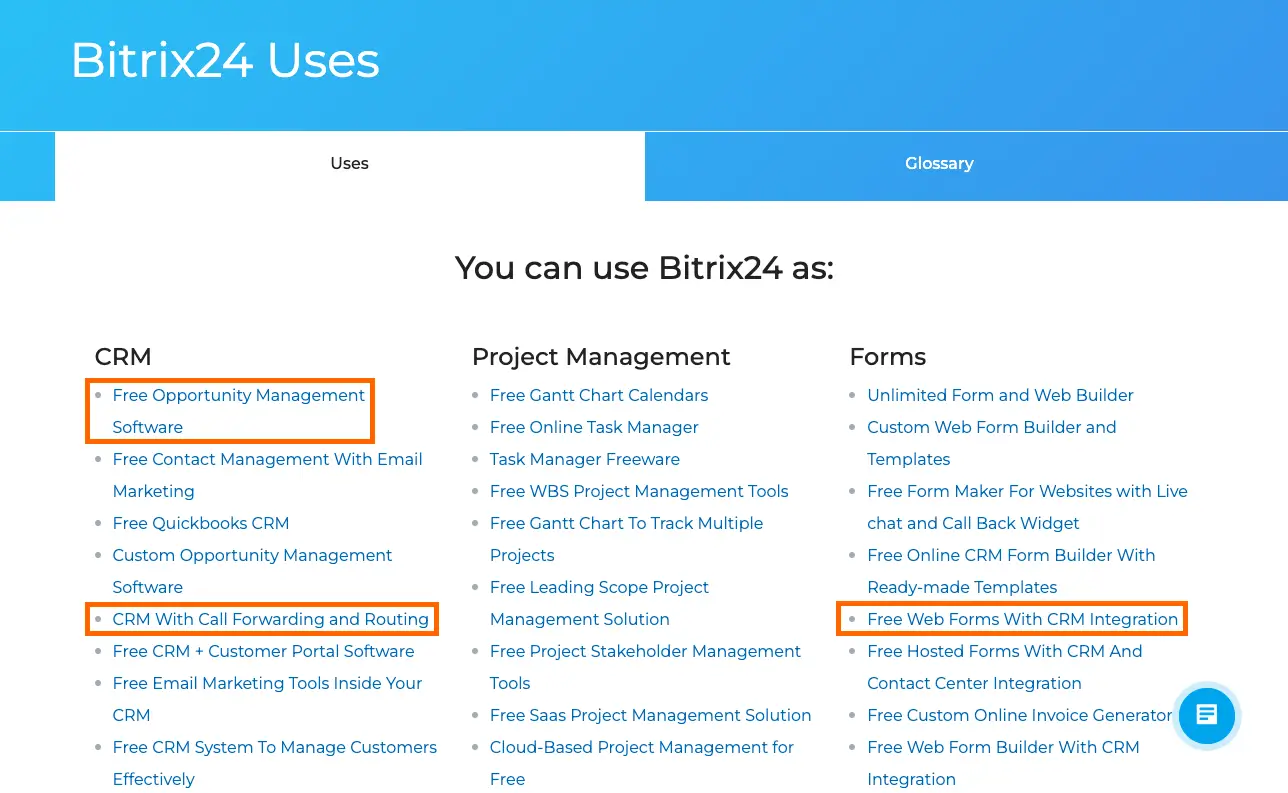
Here’s an example taken from Bitrix24 and its use case corpus page.

It’s important to note that you should not use AI to generate this corpus. Many AI services have digital watermarks in the content they generate, which serve to tell other AI that the content was artificially generated.
AI researchers don’t want their AIs trained on AI data, so if you use AI-generated content, your corpus may not be used by AI assistants.
Off-site search experience optimization
Unlike search engines, generative AIs use pattern matching just as much, if not more, than domain authority to recommend content.
Off-site search experience optimization is important and entails placing descriptions of what your brand is used for in places that are likely to be scraped by the AI. You will want these descriptions and use cases to be the most important ones you have included on your website. This is to reinforce that your brand is used for your most profitable use cases (assuming competition isn’t too steep).
The AIs don’t use every website, but there are some you can be sure they rely on for their information.
These include top message boards or any blog with sufficient enough traffic to be included in a search engine’s index. Oftentimes, AI assistants use similar indexes as search engines and you can even submit websites to them in the same fashion (more on this below).
Optimally, an AI will find use cases for your brand that reinforces what you have written on your website.
Technical on-site search engine optimization is just as important
As your content needs to be easily scrapable for AI assistants, a lot of the same technical requirements as search engine optimization apply to search experience optimization.
- Have a sitemap.
- Submit your website to the relevant search console (Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools).
- Use server-side rendering if you have a single page application.
- Don’t have orphan pages. Don’t nest important content too many clicks away from your homepage.
These are the bare minimum technical aspects that need to be kept in mind if you want your content to be used by AI assistants.
Knowing exploits
While there are a bunch of hacks and exploits with the current iterations of AI assistants, these will likely get patched quickly.
In the early days of commercial search engines, there were many ways that webmasters would trick the system. These all got resolved, and now whitehat SEO is the best route for any business owner who wants a long-lasting profitable company.
With this said, there are some things you can do. For example, suppose you have a business where your source of revenue is customers you refer through SEO traffic on your website.
In the past, doing standard search engine optimization and including a referral link was enough. Now, however, because AI assistants will just recommend what you are recommending and not include your referral link, this is no longer enough.
Now you’re better off not including the brand name while simultaneously including lots of text about the brand’s use case. This way, when somebody looks up the use case for the brand you are promoting, your site comes up and not the brand. A searcher then has to go to your site and click on your referral link.
For now, this seems like a way to maintain the status quo of referral-based search marketing. However, a patch for this could be developed. If AI assistants learn to follow links, they may learn that your referral links lead to another brand and then recommend that brand instead of your website. Since it is unlikely an AI assistant will include your referral link, you then will not be paid for your work, even though you helped searchers find what they wanted.
Who is search experience optimization best for?
Search experience optimization is best for brands who wish to get recommendations from AI assistants for relevant use cases.
If two brands of equal authority serve the same audience, but only one writes its use cases online, this is the one that the AI assistant will recommend. Even if the one that writes its use cases is smaller than its competitor, this one will still likely be recommended just because it invested in this new SEO.
Start on search experience optimization
It’s easy to get started with this new SEO.
Make sure you follow the technical checklist mentioned above and then start on your use case corpus generation.
AI assistants, unlike search engines, don’t require the same fluff that search engines require, such as an introduction or conclusion. Some LLMs (large language models) even use dense instruction manuals. This means you can be brutally concise and efficient with your descriptions while trying to hit every use case.
You can also get a professional to consult on search experience optimization.
This is something we do, so if you’d like to work with us, set something up below.
Or send an inquiry.